Introduction
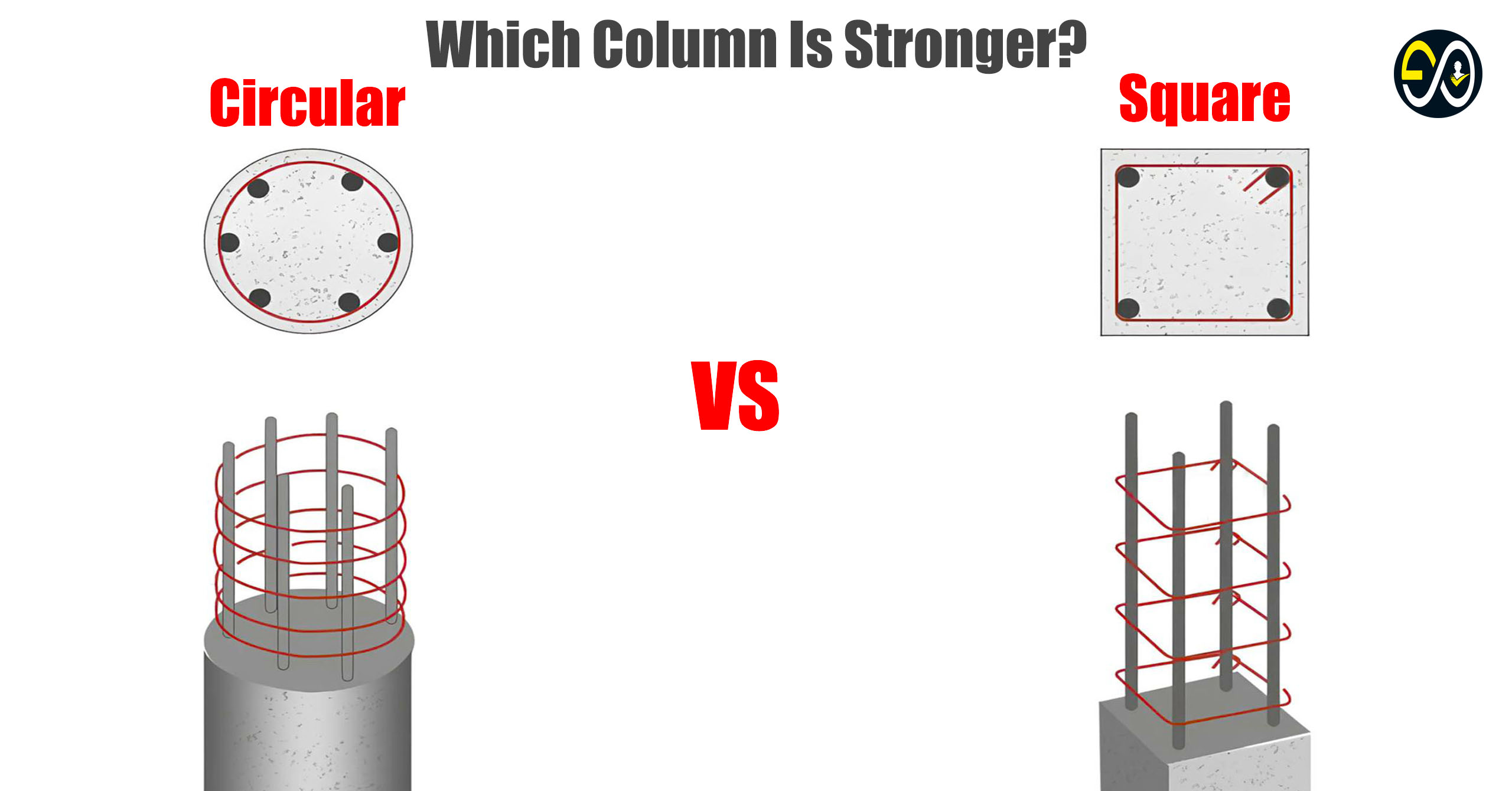
When it comes to construction, one of the most crucial components is the column. Columns are vertical structures that transfer the weight of a building or structure down to its foundation, making them essential for the stability and integrity of any construction. However, when designing a column, the shape becomes an important factor. So, which shape is stronger: circular or square? Let’s dive in to find out!
Table of Contents
What Makes a Column Strong?
The strength of a column depends on several factors, including its material, cross-sectional shape, and how well it distributes loads. A strong column efficiently transfers loads without buckling, cracking, or failing under stress. However, the shape of the column plays a significant role in how it handles these stresses.
Importance of Column Strength in Construction
Columns are the pillars that hold up buildings. Weak columns can lead to structural failures, which can be catastrophic. Therefore, understanding which column shape offers better strength is essential for architects and engineers.
Basics of Column Design
Purpose of Columns in Structures
Columns serve to support the weight of the structure above and transfer that weight down to the foundation. They are the key elements that prevent buildings from collapsing under their weight.
Factors Influencing Column Strength
Column strength is influenced by material choice (e.g., steel, concrete, or wood), the design load, and environmental factors. However, the shape of the column is one of the primary factors affecting its ability to withstand loads.
Overview of Circular Columns
Design and Structure of Circular Columns
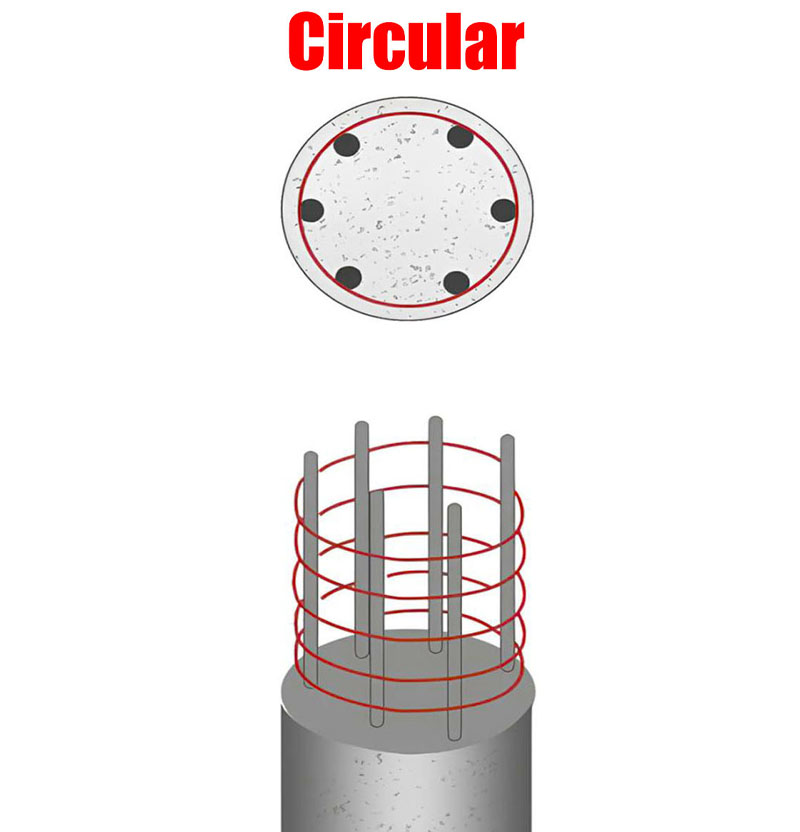
Circular columns are exactly what they sound like – columns with a circular cross-section. Their round shape provides uniform stress distribution, making them particularly strong in handling compression loads.
Advantages of Circular Columns
- Uniform load distribution: Circular columns distribute loads evenly across their surface, reducing stress concentrations.
- Better resistance to buckling: Due to their shape, circular columns are less prone to buckling under load compared to square columns.
- Aesthetic appeal: Circular columns can offer a sleek, modern look that appeals to many architects.
Overview of Square Columns
Design and Structure of Square Columns
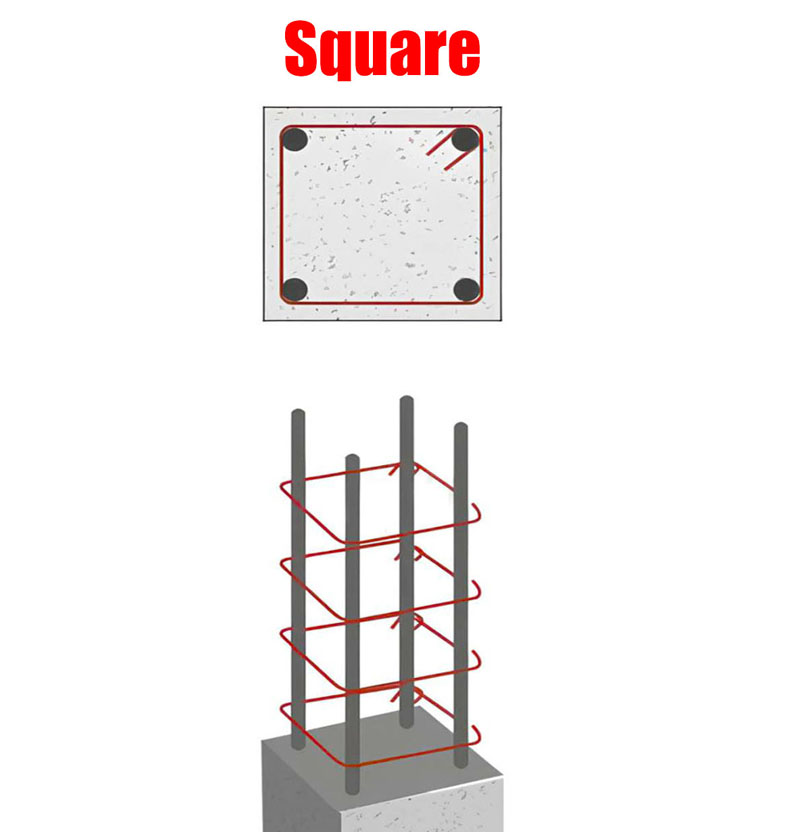
Square columns have a square cross-section and are commonly used in construction. While they don’t offer the same uniform stress distribution as circular columns, they are easier to construct and align with other building elements.
Advantages of Square Columns
- Ease of construction: Square columns are easier to form, especially when using materials like concrete.
- Efficient use of space: Square columns can be placed flush against walls or corners, maximizing usable space in a building.
- Compatibility with rectangular layouts: Most buildings have rectangular layouts and square columns fit well into these designs.
Comparison Between Circular and Square Columns
Strength Considerations
In terms of pure strength, circular columns tend to outperform square columns, especially under compression. This is due to their ability to distribute stress more evenly across their surface, reducing the chances of localized failures.
Space Efficiency and Aesthetics
While circular columns may be stronger, square columns are often more space-efficient. They fit neatly into corners and against walls, maximizing usable space in a building. Aesthetically, the choice between circular and square columns often comes down to personal preference and the design language of the building.
Load Distribution in Circular Columns
How Circular Columns Handle Compression
Circular columns excel at handling compression loads. Their round shape allows them to distribute weight evenly, reducing stress concentrations and making them less prone to failure.
Stress Distribution Patterns
The stress in a circular column is uniformly distributed across the cross-section. This uniformity reduces the likelihood of weak points developing, contributing to the overall strength of the column.
Load Distribution in Square Columns
How Square Columns Handle Compression
Square columns handle compression differently from circular columns. The corners of a square column can create stress concentrations, which can weaken the column over time.
Stress Concentration in Corners
Unlike circular columns, square columns tend to experience higher stress at their corners, which can make them more susceptible to cracking and failure under heavy loads.
Material Usage and Efficiency
Circular Columns vs. Square Columns in Material Utilization
Circular columns often use materials more efficiently, especially when handling compression. However, square columns can be more cost-effective to construct, particularly when working with standard building materials like concrete blocks.
Cost Implications of Material Usage
While circular columns may offer better performance, the additional material and labor costs associated with constructing them can make square columns a more economical choice in some cases.
Resistance to Buckling
Circular Columns’ Buckling Resistance
Circular columns have a natural advantage when it comes to resisting buckling. Their shape allows them to handle loads from all directions more effectively, reducing the risk of buckling.
Square Columns’ Buckling Resistance
Square columns are more prone to buckling, especially when subjected to eccentric loads (loads that are not applied directly along the center of the column).
Seismic Performance
Circular Columns During Earthquakes
Circular columns generally perform better during seismic events. Their ability to distribute loads evenly makes them more resilient to the lateral forces generated by earthquakes.
Square Columns During Earthquakes
Square columns can struggle during earthquakes, especially if they experience torsion or uneven loading. Their corners are more vulnerable to cracking under these conditions.
Conclusion
So, which column is stronger, circular or square? The answer depends on the context. Circular columns generally offer better strength and resistance to buckling, making them ideal for high-load applications. However, square columns are more space-efficient and cost-effective, which can make them the better choice for residential and commercial buildings. Ultimately, the best choice depends on the specific needs of the project.